basophils
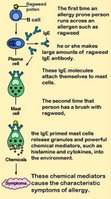
 Basophils are granulocytes packed with granules that stain basic (purple with H&E). The nucleus is bilobed, and the metachromatic granules contain sulfated glycosaminoglycans as well as vasoactive compounds – histamine and proteoglycans. Lysosomal arylsulfatase is found in granules of developing basophils in bone marrow. Basophil granules are surrounded by a unit membrane and contain particles which are uniform in size across the same granule yet vary in size in different granules within the same cell. Some granules reveal a homogeneous texture and/or "myelin" figures. [s] Though basophils and mast cells share morphological features, the appearance of most basophil granules differs from the ultrastructure of human mast cell granules.
Basophils are granulocytes packed with granules that stain basic (purple with H&E). The nucleus is bilobed, and the metachromatic granules contain sulfated glycosaminoglycans as well as vasoactive compounds – histamine and proteoglycans. Lysosomal arylsulfatase is found in granules of developing basophils in bone marrow. Basophil granules are surrounded by a unit membrane and contain particles which are uniform in size across the same granule yet vary in size in different granules within the same cell. Some granules reveal a homogeneous texture and/or "myelin" figures. [s] Though basophils and mast cells share morphological features, the appearance of most basophil granules differs from the ultrastructure of human mast cell granules.Activated basophils release proinflammatory histamine and proteoglycans from granules, and synthesize then secrete leukotrienes and cytokines (particularly IL-4). Histamine and IL-4, which is associated with production of IgE, are involved in allergic reactions.
Basophils are the least common granulocyte, representing about 0.5% to 1% of circulating leukocytes. A low basophil count combined with a low neutrophil count almost always portends leukemia.
Tables Fc receptors Immune Cytokines Immunoglobulins .
tags [Immunology][leukocytes]
Labels: basophils, bone marrow, cytokines, granulocytes, H and E, histamine, IgE, leukemia, leukocytes, leukotrienes, lysosomal arylsulfatase, mast cells, morphology, proteoglycans
| 0 Guide-Glossary