Granulocytes are granulated
leukocytes generated by
granulopoiesis in the bone marrow. Because their nuclei vary in shape (usually 3-lobed) granulocytes are also termed polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN, PML). Usually, the term polymorphonuclear leukocyte is used to designate neutrophil granulocytes, which are the most abundant of the granulocytes.
The granules are named according to their staining characteristics with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) :
● Basophil granules stain purple
● Eosinophil granules stain red
● Neutrophil granules stain a neutral pink
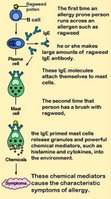 Mast cells
Mast cells contain
metachromatic granules that store
inflammatory mediators, including rich in
histamine and
heparin. Mast cells react to allergens and other degranulating agents with sequential exocytosis (
description). Mast cells function in wound healing, in
autoimmune disorders, and in the
inflammatory and
immune responses, including allergic reactions and anaphylaxis. (image at left - click to enlarge).
Mast cells are
morphologically similar to
basophils and both express
CD34, though they may have different
bone marrow precursors. Unlike basophils, masts cell
circulate in an immature form, maturing only in tissue sites where they are resident. Mast cells are found in
connective tissue of most organs, and in
mucosal tissue.
Mast cells can be activated when an
allergen binds to the
IgE that is already coating the cell. Allergens are typically proteins or polysaccharides that bind to the
Fab segment of the cognate IgE coating the mast cell surface. Crosslinking of two or more IgE molecules is required to
activate the mast cell when steric changes disturb the cell membrane structure, triggering an intracellular cascade that activates the mast cell. Although this reaction is most often encountered in allergic reactions, it apparently
evolved as a defense system against
intestinal parasitism, such as tapeworm infestations.
Mast cells express
pattern-recognition receptors plus high-affinity
receptor (
FcεRI) for
IgE, which ligates specific IgE molecules irreversibly.
On activation, mast cells degranulate, releasing preformed mediators into the interstitium:
● histamine
● proteoglycans, mainly heparin (anticoagulant)
●
serine proteases● freshly
synthesized lipid mediators (
eicosanoids)
Eicosanoid Actions :
_ ●
prostaglandin D2 (
PGD2)
_ ● leukotriene C4 (
LTC4)
●
cytokines
Complement Receptors
Cytokines
Eicosanoid Actions
Fc receptors
Immune Cytokines
Immunoglobulins
Interferons
Scavenger Receptors
Toll-like Receptors▲
Top ▲
tags
[Immunology] [WBC] [granulocyte]Labels: basophils, eosinophils, granulocytes, granulopoiesis, leukocytes, neutrophils, PML, PMN, polymorphonuclear leukocytes
|


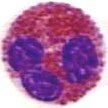 Eosinophils (acidophils) are granulocytes packed with granules that stain acidic (red with H&E). Eosinophils combat parasitic infection, and have diverse immune responsibilities.
Eosinophils (acidophils) are granulocytes packed with granules that stain acidic (red with H&E). Eosinophils combat parasitic infection, and have diverse immune responsibilities.









































